1.1 目标
- 掌握一对多关系的数据表设计方案和原理;
- 掌握多对多关系的数据表设计方案和原理;
- 掌握where子句进行数据筛选;
- 掌握group by子句进行数据分类统计;
- 掌握order by子句进行数据排序;
- 了解mysql数据库的设计规范;
1.2 实体之间的关系
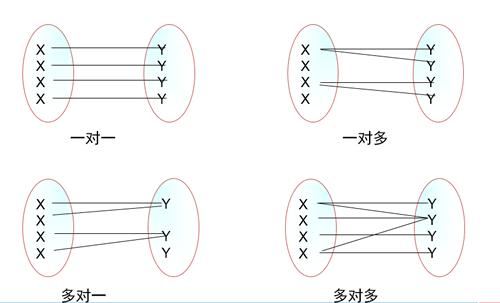
1.2.1 一对多(1:N)
主表中的一条记录对应从表中的多条记录
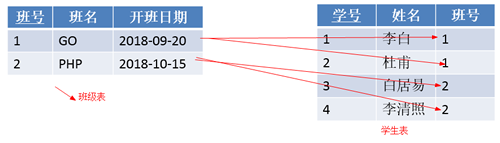
实现一对多的方式:主键和非主键建关系
问题:说出几个一对多的关系?
班主任表——学生表
品牌表——商品表1.2.2 多对一(N:1)
多对一就是一对多
1.2.3 一对一(1:1)
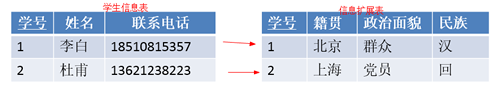
如何实现一对一:主键和主键建关系
思考:一对一两个表完全可以用一个表实现,为什么还要分成两个表?
答:在字段数量很多情况下,数据量也就很大,每次查询都需要检索大量数据,这样效率低下。我们可以将所有字段分成两个部分,“常用字段”和“不常用字段”,这样对大部分查询者来说效率提高了。【表的垂直分割】1.2.3 多对多(N:M)
主表中的一条记录对应从表中的多条记录,从表中的一条记录,对应主表中的多条记录
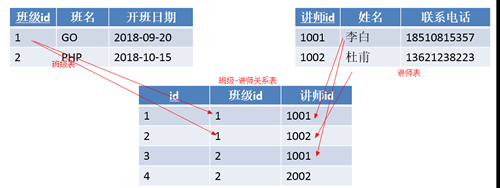
如何实现多对多:利用第三张关系表
问题:说出几个多对多的关系?
讲师表——学生表
课程表——学生表
商品表——订单表小结:
如何实现一对一:主键和主键建关系
如果实现一对多:主键和非主键建关系
如何实现多对多:引入第三张关系表1.3 数据库设计
1.3.1 数据库设计的步骤
- 收集信息:与该系统有关人员进行交流、坐谈,充分理解数据库需要完成的任务
- 标识对象(实体-Entity):标识数据库要管理的关键对象或实体
- 标识每个实体的属性(Attribute)
- 标识对象之间的关系(Relationship)
- 将模型转换成数据库
- 规范化
1.3.2 例题
第一步:收集信息
BBS论坛的基本功能:
用户注册和登录,后台数据库需要存放用户的注册信息和在线状态信息;
用户发贴,后台数据库需要存放贴子相关信息,如贴子内容、标题等;
用户可以对发帖进行回复;
论坛版块管理:后台数据库需要存放各个版块信息,如版主、版块名称、贴子数等;第二步:标识对象
实体一般是名词:
1、用户对象
2、板块对象
3、帖子对象
4、跟帖对象第三步:标识每个实体的属性
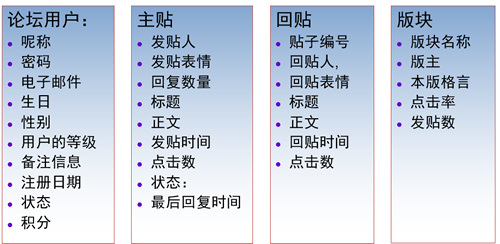
第四步:标识对象之间的关系
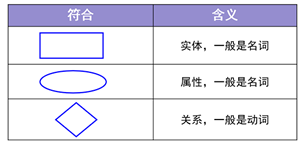
1.3.3 绘制E-R图
E-R(Entity-Relationship)实体关系图)
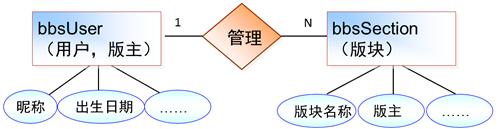
完整的E-R图
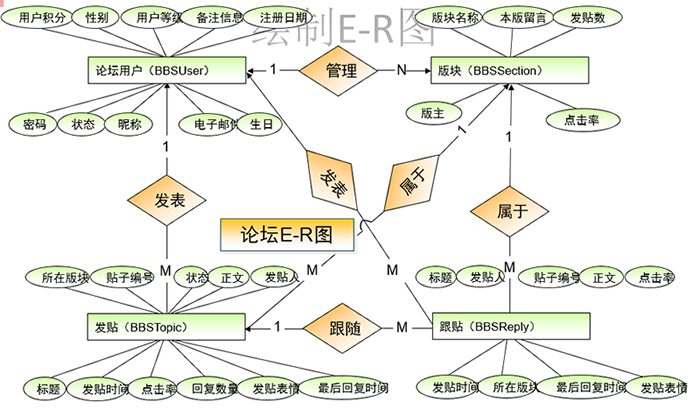
1.3.4 将E-R图转成表
- 实体转成表,属性转成字段
- 如果没有合适的字段做主键,给表添加一个自动增长列做主键。
1.4 数据规范化
1.4.1 第一范式:确保每列原则性
第一范式:的目标是确保每列的原子性,一个字段表示一个含义
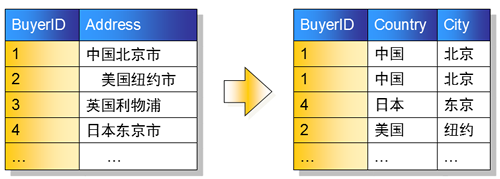
思考如下表是否满足第一范式
思考:地址包含省、市、县、地区是否需要拆分?
答:如果仅仅起地址的作用,不需要统计,可以不拆分;如果有按地区统计的功能需要拆分。
在实际项目中,建议拆分。
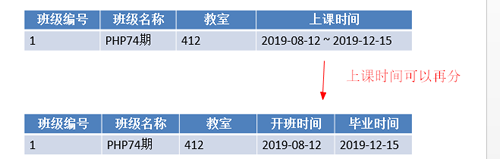
1.4.2 第二范式:非键字段必须依赖于键字段
第二范式:在满足第一范式的前提下,要求每个表只描述一件事情
思考:如下表设计是否合理

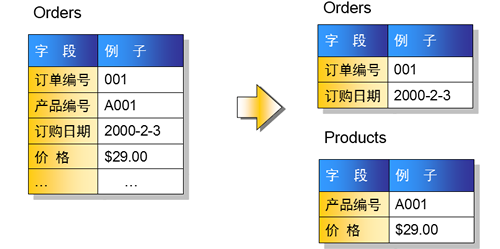
1.4.3 第三范式:消除传递依赖
第三范式:在满足第二范式的前提下,除了主键以外的其他列消除传递依赖。
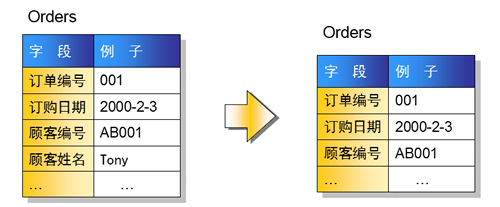
思考:如下表设计是否合理?

结论:不满足第三范式,因为语文和数学确定了,总分就确定了
1.4.4 反3NF
范式越高,数据冗余越少,但是效率有时就越地下,为了提高运行效率,可以适当让数据冗余。
| 学号 | 姓名 | 语文 | 数学 | 总分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 李白 | 77 | 88 | 165 |
上面的设计不满足第三范式,但是高考分数表就是这样设计的,为什么?
答:高考分数峰值访问量非常大,这时候就是性能更重要。当性能和规范化冲突的时候,我们首选性能。这就是“反三范式”。
小结
1、第一范式约束的所有字段
2、第二范式约束的主键和非主键的关系
3、第三范式约束的非主键之间的关系
4、范式越高,冗余越少,但表业越多。
5、规范化和性能的关系 :性能比规范化更重要
1.4.5 例题
需求
假设某建筑公司要设计一个数据库。公司的业务规
则概括说明如下:
公司承担多个工程项目,每一项工程有:工程号、工程名称、施工人员等
公司有多名职工,每一名职工有:职工号、姓名、性别、职务(工程师、技术员)等
公司按照工时和小时工资率支付工资,小时工资率由职工的职务决定(例如,技术员的小时工资率与工程师不同)标识实体
1、工程
2、职工
3、工时
4、小时工资率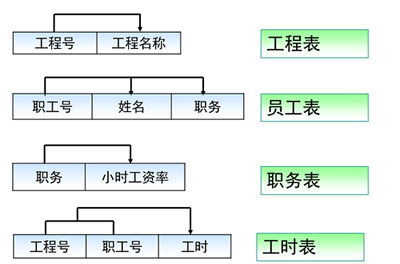
1.5 查询语句
语法:select [选项] 列名 [from 表名] [where 条件] [group by 分组] [order by 排序][having 条件] [limit 限制]1.5.1 字段表达式
-- 可以直接输出内容
mysql> select '锄禾日当午';
+------------+
| 锄禾日当午 |
+------------+
| 锄禾日当午 |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 输出表达式
mysql> select 10*10;
+-------+
| 10*10 |
+-------+
| 100 |
+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select ch,math,ch+math from stu;
+------+------+---------+
| ch | math | ch+math |
+------+------+---------+
| 80 | NULL | NULL |
| 77 | 76 | 153 |
| 55 | 82 | 137 |
| NULL | 74 | NULL |
-- 表达式部分可以用函数
mysql> select rand();
+--------------------+
| rand() |
+--------------------+
| 0.6669325378415478 |
+--------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)通过as给字段取别名
mysql> select '锄禾日当午' as '标题'; -- 取别名
+------------+
| 标题 |
+------------+
| 锄禾日当午 |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select ch,math,ch+math as '总分' from stu;
+------+------+------+
| ch | math | 总分 |
+------+------+------+
| 80 | NULL | NULL |
| 77 | 76 | 153 |
| 55 | 82 | 137 |
| NULL | 74 | NULL |
-- 多学一招:as可以省略
mysql> select ch,math,ch+math '总分' from stu;
+------+------+------+
| ch | math | 总分 |
+------+------+------+
| 80 | NULL | NULL |
| 77 | 76 | 153 |
| 55 | 82 | 137 |
| NULL | 74 | NULL |1.5.2 from子句
from:来自,from后面跟的是数据源。数据源可以有多个。返回笛卡尔积。
插入测试表
create table t1(
str char(2)
);
insert into t1 values ('aa'),('bb');
create table t2(
num int
);
insert into t2 values (10),(20);测试
-- from子句
mysql> select * from t1;
+------+
| str |
+------+
| aa |
| bb |
+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 多个数据源,返回笛卡尔积
mysql> select * from t1,t2;
+------+------+
| str | num |
+------+------+
| aa | 10 |
| bb | 10 |
| aa | 20 |
| bb | 20 |
+------+------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)1.5.3 dual表
dual表是一个伪表。在有些特定情况下,没有具体的表的参与,但是为了保证select语句的完整又必须要一个表名,这时候就使用伪表。
mysql> select 10*10 as 结果 from dual;
+------+
| 结果 |
+------+
| 100 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)1.5.4 where子句
where后面跟的是条件,在数据源中进行筛选。返回条件为真记录
MySQL支持的运算符
-- 比较运算符
> 大于
< 小于
>= 大于等于
<= 小于等于
= 等于
!= 不等于
-- 逻辑运算符
and 与
or 或
not 非
-- 其他
in | not in 字段的值在枚举范围内
between…and|not between…and 字段的值在数字范围内
is null | is not null 字段的值不为空例题:
-- 查找语文成绩及格的学生
mysql> select * from stu where ch>=60;
-- 查询语文和数学都及格的学生
mysql> select * from stu where ch>=60 and math>=60;
-- 查询语文或数学不及格的学生
mysql> select * from stu where ch<60 or math<60;思考:如下语句输出什么?
mysql> select * from stu where 1; -- 输出所有数据
mysql> select * from stu where 0; -- 不输出数据思考:如何查找北京和上海的学生
-- 通过or实现
mysql> select * from stu where stuaddress='北京' or stuaddress='上海';
-- 通过in语句实现
mysql> select * from stu where stuaddress in ('北京','上海');
-- 查询不是北京和上海的学生
mysql> select * from stu where stuaddress not in ('北京','上海');思考:查找年龄在20~25之间
-- 方法一:
mysql> select * from stu where stuage>=20 and stuage<=25;
-- 方法二:
mysql> select * from stu where not(stuage<20 or stuage>25);
-- 方法三:between...and...
mysql> select * from stu where stuage between 20 and 25;
-- 年龄不在20~25之间
mysql> select * from stu where stuage not between 20 and 25;思考:
-- 查找缺考的学生
mysql> select * from stu where ch is null or math is null;
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
| s25304 | 欧阳俊雄 | 男 | 28 | 4 | 天津 | NULL | 74 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
-- 查找没有缺考的学生
mysql> select * from stu where ch is not null and math is not null;
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 |
| s25303 | 李斯文 | 女 | 22 | 2 | 北京 | 55 | 82 |
| s25305 | 诸葛丽丽 | 女 | 23 | 7 | 河南 | 72 | 56 |
| s25318 | 争青小子 | 男 | 26 | 6 | 天津 | 86 | 92 |
| s25319 | 梅超风 | 女 | 23 | 5 | 河北 | 74 | 67 |
| s25320 | Tom | 男 | 24 | 8 | 北京 | 65 | 67 |
| s25321 | Tabm | 女 | 23 | 9 | 河北 | 88 | 77 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 查找需要补考的学生
mysql> select * from stu where ch<60 or math<60 or ch is null or math is null;
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
| s25303 | 李斯文 | 女 | 22 | 2 | 北京 | 55 | 82 |
| s25304 | 欧阳俊雄 | 男 | 28 | 4 | 天津 | NULL | 74 |
| s25305 | 诸葛丽丽 | 女 | 23 | 7 | 河南 | 72 | 56 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)练习:
-- 1、查找学号是s25301,s25302,s25303的学生
mysql> select * from stu where stuno in ('s25301','s25302','s25303');
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 |
| s25303 | 李斯文 | 女 | 22 | 2 | 北京 | 55 | 82 |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 2、查找年龄是18~20的学生
mysql> select * from stu where stuage between 18 and 20;
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)1.5.5 group by 【分组查询】
将查询的结果分组,分组查询目的在于统计数据。
-- 查询男生和女生的各自语文平均分
mysql> select stusex,avg(ch) '平均分' from stu group by stusex;
+--------+---------+
| stusex | 平均分 |
+--------+---------+
| 女 | 72.2500 |
| 男 | 77.0000 |
+--------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 查询男生和女生各自多少人
mysql> select stusex,count(*) 人数 from stu group by stusex;
+--------+------+
| stusex | 人数 |
+--------+------+
| 女 | 4 |
| 男 | 5 |
+--------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 查询每个地区多少人
mysql> select stuaddress,count(*) from stu group by stuaddress;
+------------+----------+
| stuaddress | count(*) |
+------------+----------+
| 上海 | 1 |
| 北京 | 3 |
| 天津 | 2 |
| 河北 | 2 |
| 河南 | 1 |
+------------+----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 每个地区的数学平均分
mysql> select stuaddress,avg(math) from stu group by stuaddress;
+------------+-----------+
| stuaddress | avg(math) |
+------------+-----------+
| 上海 | 76.0000 |
| 北京 | 74.5000 |
| 天津 | 83.0000 |
| 河北 | 72.0000 |
| 河南 | 56.0000 |
+------------+-----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)查询字段是普通字段,只取第一个值
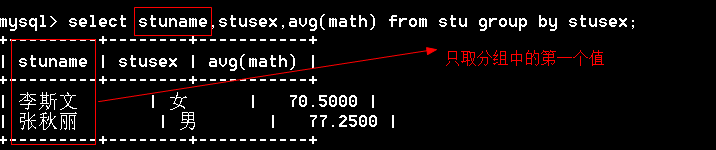
通过group_concat()函数将同一组的值连接起来显示
mysql> select group_concat(stuname),stusex,avg(math) from stu group by stusex;
+-------------------------------------+--------+-----------+
| group_concat(stuname) | stusex | avg(math) |
+-------------------------------------+--------+-----------+
| 李斯文,诸葛丽丽,梅超风,Tabm | 女 | 70.5000 |
| 张秋丽,李文才,欧阳俊雄,争青小子,Tom | 男 | 77.2500 |
+-------------------------------------+--------+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)多列分组
mysql> select stuaddress,stusex,avg(math) from stu group by stuaddress,stusex;
+------------+--------+-----------+
| stuaddress | stusex | avg(math) |
+------------+--------+-----------+
| 上海 | 男 | 76.0000 |
| 北京 | 女 | 82.0000 |
| 北京 | 男 | 67.0000 |
| 天津 | 男 | 83.0000 |
| 河北 | 女 | 72.0000 |
| 河南 | 女 | 56.0000 |
+------------+--------+-----------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)小结:
1、如果是分组查询,查询字段是分组字段和聚合函数。
2、查询字段是普通字段,只取第一个值
3、group_concat()将同一组的数据连接起来1.5.6 order by排序
asc:升序【默认】
desc:降序
-- 按年龄的升序排列
mysql> select * from stu order by stuage asc;
mysql> select * from stu order by stuage; -- 默认是升序
-- 按总分降序
mysql> select *,ch+math '总分' from stu order by ch+math desc;多列排序
-- 年龄升序,如果年龄一样,按ch降序排列
mysql> select * from stu order by stuage asc,ch desc;思考如下代码表示什么含义
select * from stu order by stuage desc,ch desc; #年龄降序,语文降序
select * from stu order by stuage desc,ch asc; #年龄降序,语文升序
select * from stu order by stuage,ch desc; #年龄升序、语文降序
select * from stu order by stuage,ch; #年龄升序、语文升序1.5.7 having条件
having:是在结果集上进行条件筛选
例题
-- 查询女生
mysql> select * from stu where stusex='女';
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25303 | 李斯文 | 女 | 22 | 2 | 北京 | 55 | 82 |
| s25305 | 诸葛丽丽 | 女 | 23 | 7 | 河南 | 72 | 56 |
| s25319 | 梅超风 | 女 | 23 | 5 | 河北 | 74 | 67 |
| s25321 | Tabm | 女 | 23 | 9 | 河北 | 88 | 77 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 查询女生
mysql> select * from stu having stusex='女';
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25303 | 李斯文 | 女 | 22 | 2 | 北京 | 55 | 82 |
| s25305 | 诸葛丽丽 | 女 | 23 | 7 | 河南 | 72 | 56 |
| s25319 | 梅超风 | 女 | 23 | 5 | 河北 | 74 | 67 |
| s25321 | Tabm | 女 | 23 | 9 | 河北 | 88 | 77 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 查询女生姓名
mysql> select stuname from stu where stusex='女';
+----------+
| stuname |
+----------+
| 李斯文 |
| 诸葛丽丽 |
| 梅超风 |
| Tabm |
+----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 使用having报错,因为结果集中没有stusex字段
mysql> select stuname from stu having stusex='女';
ERROR 1054 (42S22): Unknown column 'stusex' in 'having clause'小结:having和where的区别:
where是对原始数据进行筛选,having是对记录集进行筛选。
1.5.8 limit
语法:limit [起始位置],显示长度
-- 从第0个位置开始取,取3条记录
mysql> select * from stu limit 0,3;
-- 从第2个位置开始取,取3条记录
mysql> select * from stu limit 2,3;
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25303 | 李斯文 | 女 | 22 | 2 | 北京 | 55 | 82 |
| s25304 | 欧阳俊雄 | 男 | 28 | 4 | 天津 | NULL | 74 |
| s25305 | 诸葛丽丽 | 女 | 23 | 7 | 河南 | 72 | 56 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)起始位置可以省略,默认是从0开始
mysql> select * from stu limit 3;
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 |
| s25303 | 李斯文 | 女 | 22 | 2 | 北京 | 55 | 82 |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)例题:找出班级总分前三名
mysql> select *,ch+math total from stu order by (ch+math) desc limit 0,3;
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+-------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math | total |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+-------+
| s25318 | 争青小子 | 男 | 26 | 6 | 天津 | 86 | 92 | 178 |
| s25321 | Tabm | 女 | 23 | 9 | 河北 | 88 | 77 | 165 |
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 | 153 |
+--------+----------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)多学一招:limit在update和delete语句中也是可以使用的。
-- 前3名语文成绩加1分
mysql> update stu set ch=ch+1 order by ch+math desc limit 3;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 3 Changed: 3 Warnings: 0
-- 前3名删除
mysql> delete from stu order by ch+math desc limit 3;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)1.5.9 查询语句中的选项
查询语句中的选项有两个:
1、 all:显示所有数据 【默认】
2、 distinct:去除结果集中重复的数据
mysql> select all stuaddress from stu;
+------------+
| stuaddress |
+------------+
| 北京 |
| 北京 |
| 天津 |
| 河南 |
| 河北 |
| 北京 |
+------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 去除重复的项
mysql> select distinct stuaddress from stu;
+------------+
| stuaddress |
+------------+
| 北京 |
| 天津 |
| 河南 |
| 河北 |
+------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)1.6 聚合函数
- sum() 求和
- avg() 求平均值
- max() 求最大值
- min() 求最小值
- count() 求记录数
# 语文最高分
mysql> select max(ch) '语文最大值' from stu;
+------------+
| 语文最大值 |
+------------+
| 88 |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
#求语文总分、语文平均分、语文最低分、总人数
mysql> select max(ch) 语文最高分,min(ch) 语文最低分,sum(ch) 语文总分,avg(ch) 语文平均分,count(*) 总人数 from stu;
+------------+------------+----------+------------+--------+
| 语文最高分 | 语文最低分 | 语文总分 | 语文平均分 | 总人数 |
+------------+------------+----------+------------+--------+
| 88 | 55 | 597 | 74.6250 | 9 |
+------------+------------+----------+------------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)1.7 模糊查询
1.7.1 通配符
- _ [下划线] 表示任意一个字符
- % 表示任意字符
练习
1、满足“T_m”的有(A、C)
A:Tom B:Toom C:Tam D:Tm E:Tmo
2、满足“T_m_”的有( B C)
A:Tmom B:Tmmm C:T1m2 D:Tmm E:Tm
3、满足“张%”的是(ABCD)
A:张三 B:张三丰 C:张牙舞爪 D:张 E:小张
4、满足“%诺基亚%”的是(ABCD)
A:诺基亚2100 B:2100诺基亚 C:把我的诺基亚拿过来 D:诺基亚1.7.2 模糊查询(like)
模糊查询的条件不能用'=',要使用like。
mysql> select * from stu where stuname like 'T_m';
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25320 | Tom | 男 | 24 | 8 | 北京 | 65 | 67 |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 查询姓张的学生
mysql> select * from stu where stuname like '张%';
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25301 | 张秋丽 | 男 | 18 | 1 | 北京 | 80 | NULL |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)1.8 union(联合)
插入测试数据
create table emp(
id tinyint unsigned auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
skill set('PHP','mysql','java')
);
insert into emp values (null,'李白',1),(null,'杜甫',2),(null,'白居易',4)
insert into emp values (null,'争青小子',3)1.8.1 union的使用
作用:将多个select语句结果集纵向联合起来
语法:select 语句 union [选项] select 语句 union [选项] select 语句-- 查询stu表中的姓名和emp表中姓名 结果自动合并的重复的记录
mysql> select stuname from stu union select name from emp;例题:查询上海的男生和北京的女生
-- 方法一:
mysql> select * from stu where (stuaddress='上海' and stusex='男') or (stuaddress='北京' and stusex='女');
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 |
| s25303 | 李斯文 | 女 | 22 | 2 | 北京 | 55 | 82 |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 方法二:union
mysql> select * from stu where stuaddress='上海' and stusex='男' union select * from stu where stuaddress='北京' and stusex='女';
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| stuNo | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuSeat | stuAddress | ch | math |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
| s25302 | 李文才 | 男 | 31 | 3 | 上海 | 77 | 76 |
| s25303 | 李斯文 | 女 | 22 | 2 | 北京 | 55 | 82 |
+--------+---------+--------+--------+---------+------------+------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
结论:union可以将一个复杂的条件转成两个简单的条件1.8.2 union的选项
union的选项有两个
1、 all:显示所有数据
2、 distinct:去除重复的数据【默认】
mysql> select stuname from stu union all select name from emp;1.8.3 union的注意事项
1、 union两边的select语句的字段个数必须一致
2、 union两边的select语句的字段名可以不一致,最终按第一个select语句的字段名。
3、 union两边的select语句中的数据类型可以不一致。
1.9 补充
1.9.1 插入数据时主键冲突
-- 插入测试表
mysql> create table stu(
-> id char(4) primary key,
-> name varchar(20)
-> )engine=innodb;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
-- 插入测试数据
mysql> insert into stu values ('s001','tom');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)如果插入的主键重复会报错
解决方法:如果插入的主键重复就执行替换
语法一:
mysql> replace into stu values('s002','ketty');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)
# 原理:如果插入的主键不重复就直接插入,如果主键重复就替换(删除原来的记录,插入新记录)语法二(推荐):
on duplicate key update # 当插入的值与主键或唯一键有冲突执行update操作
-- 例题
mysql> insert into stu values ('s002','李白') on duplicate key update name='李白';
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)
# 插入的数据和主键或唯一键起冲突,将s002的name字段改为‘李白’
评论 (0)