1.1 目标
- 掌握char和varchar的应用;
- 了解text类型是用来存储长文本数据;
- 了解字段属性的作用;
- 掌握主键primary key的应用以及效果;
- 掌握逻辑主键的自增长auto_increment应用;
- 掌握唯一键与主键的区别;
- 了解外键的约束作用;
- 掌握主键冲突的两种解决方案;
1.2 数据类型
MySQL中的数据类型是强类型
1.2.1 数值型
1、 整型
| 整形 | 占用字节数 | 范围 |
|---|---|---|
| tinyint | 1 | -128~127 |
| smallint | 2 | -32768~32767 |
| mediumint | 3 | -8388608~8388607 |
| int | 4 | -2147483648~2147483647 |
| bigint | 8 | -9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807 |
选择的范围尽可能小,范围越小占用资源越少
mysql> create table stu1(
-> id tinyint, # 范围要尽可能小,范围越小,占用空间越少
-> name varchar(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
-- 超出范围会报错
mysql> insert into stu1 values (128,'tom');
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'id' at row 1无符号整形(unsigned) 无符号整形就是没有负数,无符号整数是整数的两倍
mysql> create table stu2(
-> id tinyint unsigned # 无符号整数
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> insert into stu2 values (128);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)整形支持显示宽度,显示宽带是最小的显示位数,如int(11)表示整形最少用11位表示,如果不够位数用0填充。显示宽度默认不起作用,必须结合zerofill才起作用。
mysql> create table stu4(
-> id int(5),
-> num int(5) zerofill # 添加前导0,int(5)显示宽带是5
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> insert into stu4 values (12,12);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from stu4;
+------+-------+
| id | num |
+------+-------+
| 12 | 00012 |
+------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)小结:
1、范围要尽可能小,范围越小,占用空间越少
2、无符号整数是整数的两倍
3、整形支持显示宽度,显示宽带是最小的显示位数,必须结合zerofill才起作用2、浮点型
| 浮点型 | 占用字节数 | 范围 |
|---|---|---|
| float(单精度型) | 4 | -3.4E+38~3.4E+38 |
| double(双精度型) | 8 | -1.8E+308~1.8E+308 |
浮点型的声明:float(M,D) double(M,D)
M:总位数 D:小数位数例题
mysql> create table stu5(
-> num1 float(5,2), -- 浮点数
-> num2 double(6,1) -- 双精度数
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> insert into stu5 values (3.1415,12.96);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from stu5;
+------+------+
| num1 | num2 |
+------+------+
| 3.14 | 13.0 |
+------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)MySQL浮点数支持科学计数法
mysql> create table stu6(
-> num float # 不指定位数,默认是小数点后面6位 double默认是17位
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> insert into stu6 values (5E2),(6E-2); # 插入科学计数法
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from stu6;
+------+
| num |
+------+
| 500 |
| 0.06 |
+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)浮点数精度会丢失
mysql> insert into stu6 values(99.999999999);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from stu6;
+------+
| num |
+------+
| 100 |
+------+小结:
1、浮点数有单精度和双精度
2、浮点数支持科学计数法
3、浮点数精度会丢失3、小数(定点数)
原理:将整数部分和小数部分分开存储
语法:
decimal(M,D)例题:
mysql> create table stu8(
-> num decimal(20,9) # 存放定点数
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into stu8 values(12.999999999);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from stu8;
+--------------+
| num |
+--------------+
| 12.999999999 |
+--------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)小结:
1、decimal是变长的,大致是每9个数字用4个字节存储,整数和小数分开计算。M最大是65,D最大是30,默认是(10,2)。
2、定点和浮点都支持无符号、显示宽度0填充。1.2.2 字符型
在数据库中没有字符串概念,只有字符,所以数据库中只能用单引号
| 数据类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| char | 定长字符,最大可以到255 |
| varchar | 可变长度字符,最大可以到65535 |
| tinytext | 2^8^–1 =255 |
| text | 2^16^–1 =65535 |
| mediumtext | 2^24^–1 |
| longtext | 2^32^–1 |
char(4):存放4个字符,中英文一样。
varchar(L)实现变长机制,需要额外的空间来记录数据真实的长度。
L的理论长度是65535,但事实上达不到,因为有的字符是多字节字符,所以L达不到65535。


text系列的类型在表中存储的是地址,占用大小大约10个字节

一个记录的所有字段的总长度也不能超过65535个字节。
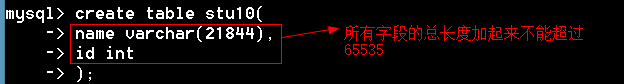
小结:
1、char是定长,var是变长
2、char最大值是255,varchar最大值是65535,具体要看字符编码
3、text系列在表中存储的是地址
4、一条记录的总长度不能超过655351.2.3 枚举(enum)
从集合中选择一个值作为数据(单选)
mysql> create table stu12(
-> name varchar(20),
-> sex enum('男','女','保密') # 枚举
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
-- 插入的枚举值只能是枚举中提供的选项
mysql> insert into stu12 values ('tom','男');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
-- 报错,只能插入男、女、保密
mysql> insert into stu12 values ('tom','不告诉你');
ERROR 1265 (01000): Data truncated for column 'sex' at row 1枚举值是通过整形数字来管理的,第一个值是1,第二个值是2,以此类推,枚举值在数据库存储的是整形数字。
mysql> insert into stu12 values ('berry',2); -- 插入数字
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from stu12;
+-------+------+
| name | sex |
+-------+------+
| tom | 男 |
| berry | 女 |
+-------+------+
mysql> select * from stu12 where sex=2; -- 2表示第二个枚举值
+-------+------+
| name | sex |
+-------+------+
| berry | 女 |
+-------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)枚举优点:
(1)、限制值
(2)、节省空间
(3)、运行速度快(整形比字符串运行速度快)思考:已知枚举占用两个字节,所以最多可以有多少个枚举值?
答:2字节=16位,2^16^=65536,范围是(0-65535),由于枚举从1开始,所以枚举值最多有65535个
1.2.4 集合(set)
从集合中选择一些值作为数据(多选)
mysql> create table stu13(
-> name varchar(20),
-> hobby set('爬山','读书','游泳','烫头') -- 集合
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into stu13 values ('tom','爬山');
mysql> insert into stu13 values ('Berry','爬山,游泳');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into stu13 values ('Berry','游泳,爬山'); -- 插入的顺序不一样,但显示的顺序一样
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from stu13;
+-------+-----------+
| name | hobby |
+-------+-----------+
| tom | 爬山 |
| Berry | 爬山,游泳 |
| Berry | 爬山,游泳 |
+-------+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)集合和枚举一样,也为每个集合元素分配一个固定值,分配方式是从前往后按2的0、1、2、…次方,转换成二进制后只有一位是1,其他都是0。
'爬山','读书','游泳','烫头'
1 2 4 8
mysql> select hobby+0 from stu13;
+---------+
| hobby+0 |
+---------+
| 1 |
| 5 |
| 5 |
+---------+
mysql> insert into stu13 values ('rose',15);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)已知集合类型占8个字节,那么集合中最多有多少选项
答:有64个选项。
1.2.5 日期时间型
| 数据类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| datetime | 日期时间,占用8个字节 |
| date | 日期 占用3个字节 |
| time | 时间 占用3个字节 |
| year | 年份,占用1个字节 |
| timestamp | 时间戳,占用4个字节 |
1、datetime和date
datetime格式:年-月-日 小时:分钟:秒。支持的范围是'1000-01-01 00:00:00'到'9999-12-31
23:59:59'。
mysql> create table stu14(
-> t1 datetime, -- 日期时间
-> t2 date -- 日期
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
-- 插入测试数据
mysql> insert into stu14 values ('2019-01-15 12:12:12','2019-01-15 12:12:12');
Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
-- 查询
mysql> select * from stu14;
+---------------------+------------+
| t1 | t2 |
+---------------------+------------+
| 2019-01-15 12:12:12 | 2019-01-15 |
+---------------------+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)2、timestamp(时间戳)
datetime类型和timestamp类型表现上是一样的,他们的区别在于:
datetime从1000到9999,而timestamp从1970年~2038年(原因在于timestamp占用4个字节,和整形的范围一样,2038年01月19日11:14:07以后的秒数就超过了4个字节的长度)
mysql> create table stu15(
-> t1 timestamp
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
mysql> insert into stu15 values ('2038-01-19 11:14:07');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)3、year
只能表示1901~2155之间的年份,因为只占用1个字节,只能表示255个数
mysql> create table stu16(
-> y1 year
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec)
mysql> insert into stu16 values (2155);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)4、time
可以表示时间,也可以表示时间间隔。范围是:-838:59:59~838:59:59
mysql> create table stu17(
-> t1 time
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> insert into stu17 values ('12:12:12');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into stu17 values ('212:12:12');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into stu17 values ('-212:12:12');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into stu17 values ('839:00:00'); -- 报错
ERROR 1292 (22007): Incorrect time value: '839:00:00' for column 't1' at row 1
-- time支持以天的方式来表示时间间隔
mysql> insert into stu17 values ('10 10:25:25'); -- 10天10小时25分25秒
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from stu17;
+------------+
| t1 |
+------------+
| 12:12:12 |
| 212:12:12 |
| -212:12:12 |
| 250:25:25 |
+------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)1.2.6 Boolean
MySQL不支持布尔型,true和false在数据库中对应的是1和0
mysql> create table stu18(
-> flag boolean
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> desc stu18;
+-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| flag | tinyint(1) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into stu18 values (true),(false);
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from stu18;
+------+
| flag |
+------+
| 1 |
| 0 |
+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec小结:
boolean型在MySQL中对应的是tinyint。
1.2.6 练习题
电话号码一般使用什么数据类型存储? varchar
手机号码用什么数据类型 char
性别一般使用什么数据类型存储? char tinyint enum
年龄信息一般使用什么数据类型存储? tinyint
照片信息一般使用什么数据类型存储? binary
薪水一般使用什么数据类型存储? decimal1.3 列属性
1.3.1 是否为空(null|not null)
null表示字段值可以为null
not null字段值不能为空练习
学员姓名允许为空吗? not null
家庭地址允许为空吗? not null
电子邮件信息允许为空吗? null
考试成绩允许为空吗? null1.3.2 默认值(default)
如果一个字段没有插入值,可以默认插入一个指定的值
mysql> create table stu19(
-> name varchar(20) not null default '姓名不详',
-> addr varchar(50) not null default '地址不详'
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> insert into stu19(name) values ('tom');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into stu19 values (default,default);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from stu19;
+----------+----------+
| name | addr |
+----------+----------+
| tom | 地址不详 |
| 姓名不详 | 地址不详 |
+----------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)小结:
default关键字用来插入默认值
1.3.3 自动增长(auto_increment)
字段值从1开始,每次递增1,自动增长的值就不会有重复,适合用来生成唯一的id。在MySQL中只要是自动增长列必须是主键
1.3.4 主键(primary key)
主键概念:唯一标识表中的记录的一个或一组列称为主键。
特点:
1、不能重复、不能为空
2、一个表只能有一个主键。作用:
1、保证数据完整性
2、加快查询速度选择主键的原则
最少性:尽量选择单个键作为主键
稳定性:尽量选择数值更新少的列作为主键
比如:学号,姓名、地址 这三个字段都不重复,选哪个做主键
选学号,因为学号最稳定练习
-- 创建主键方法一
mysql> create table stu20(
-> id int auto_increment primary key,
-> name varchar(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)
-- 创建主键方法二
mysql> create table stu21(
-> id int auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20),
-> primary key(id)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)组合键
mysql> create table stu22(
-> classname varchar(20),
-> stuname varchar(20),
-> primary key(classname,stuname) -- 创建组合键
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> desc stu22;
+-----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| classname | varchar(20) | NO | PRI | | |
| stuname | varchar(20) | NO | PRI | | |
+-----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)通过更改表添加主键
mysql> create table stu23(
-> id int,
-> name varchar(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
-- 添加主键
mysql> alter table stu23 add primary key(id);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.09 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0删除主键
mysql> alter table stu23 drop primary key;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0插入数据
mysql> create table stu25(
-> id tinyint unsigned auto_increment primary key,
-> name varchar(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
-- 插入数据
mysql> insert into stu25 values (3,'tom'); -- 可以直接插入数字
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.06 sec)
-- 自动增长列可以插入null,让列的值自动递增
mysql> insert into stu25 values (null,'berry');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)小结:
1、只要是auto_increment必须是主键,但是主键不一定是auto_increment
2、主键特点是不能重复不能为空
3、一个表只能有一个主键,但是一个主键可以有多个字段组成
4、自动增长列通过插入null值让其递增
5、自动增长列的数据被删除,默认不再重复使用。truncate table删除数据后,再次插入从1开始
练习
在主键列输入的数值,允许为空吗? 不可以
一个表可以有多个主键吗? 不可以
在一个学校数据库中,如果一个学校内允许重名的学员,但是一个班级内不允许学员重名,可以组合班级和姓名两个字段一起来作为主键吗? 对
标识列(自动增长列)允许为字符数据类型吗? 不允许
一个自动增长列中,插入3行,删除2行,插入3行,删除2行,插入3行,删除2行,再次插入是多少? 101.3.5 唯一键(unique)
| 键 | 区别 |
|---|---|
| 主键 | 1、不能重复,不能为空 2、一个表只能有一个主键 |
| 唯一键 | 1、不能重刻,可以为空 2、一个表可以有多个唯一键 |
例题
-- 创建表的时候创建唯一键
mysql> create table stu26(
-> id int auto_increment primary key,
-> name varchar(20) unique -- 唯一键
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
-- 方法二
mysql> create table stu27(
-> id int primary key,
-> name varchar(20),
-> unique(name)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
多学一招:
unique 或 unique key 是一样的通过修改表添加唯一键
-- 将name设为唯一键
mysql> alter table stu28 add unique(name);
-- 将name,addr设为唯一键
mysql> alter table stu28 add unique(name),add unique(addr);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> desc stu28;
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | UNI | NULL | |
| addr | varchar(20) | YES | UNI | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.02 sec)通过show create table 查看唯一键的名字
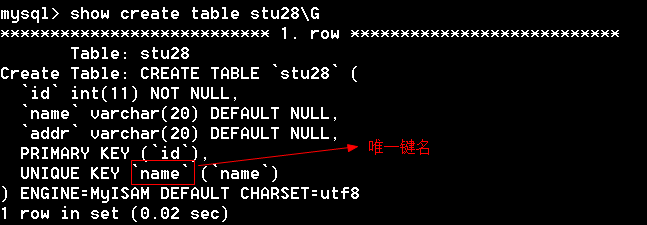
通过唯一键的名字删除唯一键
mysql> alter table stu28 drop index name;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 01.3.6 备注(comment)
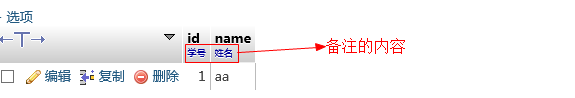
说明性文本
mysql> create table stu29(
-> id int primary key comment '学号',
-> name varchar(20) not null comment '姓名'
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)注意:备注属于SQL代码的一部分
1.4 SQL注释
单行注释
-- 单行注释
# 单行注释
多行注释 /* */
1.5 数据完整性
1.5.1 数据完整性包括
1、实体完整性
1、主键约束
2、唯一约束
3、标识列2、 域完整性
1、数据类型约束
2、非空约束
3、默认值约束3、 引用完整性
外键约束4、 自定义完整性
1、存储过程
2、触发器1.5.2 主表和从表
- 主表中没有的记录,从表不允许插入
- 从表中有的记录,主表中不允许删除
- 删除主表前,先删子表
1.5.3 外键(foreign key)
外键:从表中的公共字段
-- 创建表的时候添加外键
drop table if exists stuinfo;
create table stuinfo(
id tinyint primary key,
name varchar(20)
)engine=innodb;
drop table if exists stuscore;
create table stuscore(
sid tinyint primary key,
score tinyint unsigned,
foreign key(sid) references stuinfo(id) -- 创建外键
)engine=innodb;
-- 通过修改表的时候添加外键
语法:alter table 从表 add foreign key(公共字段) references 主表(公共字段)
drop table if exists stuinfo;
create table stuinfo(
id tinyint primary key,
name varchar(20)
)engine=innodb;
drop table if exists stuscore;
create table stuscore(
sid tinyint primary key,
score tinyint unsigned
)engine=innodb;
alter table stuscore add foreign key (sid) references stuinfo(id)删除外键
通过外键的名字删除外键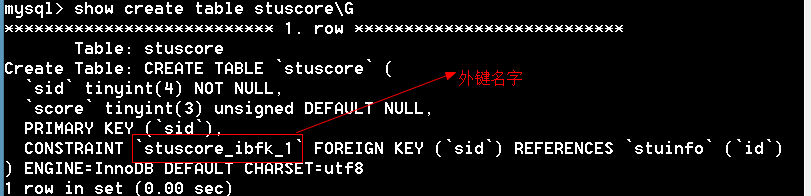
-- 删除外键
mysql> alter table stuscore drop foreign key `stuscore_ibfk_1`;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0小结:
1、只有innodb才能支持外键
2、公共字段的名字可以不一样,但是数据类型要一样1.5.4 三种外键操作
1、 严格限制(参见主表和从表)
2、 置空操作(set null):如果主表记录删除,或关联字段更新,则从表外键字段被设置为null。
3、 级联操作(cascade):如果主表记录删除,则从表记录也被删除。主表更新,从表外键字段也更新。
语法:foreign key (外键字段) references 主表名 (关联字段) [主表记录删除时的动作] [主表记录更新时的动作]。
一般说删除时置空,更新时级联。
drop table if exists stuinfo;
create table stuinfo(
id tinyint primary key comment '学号,主键',
name varchar(20) comment '姓名'
)engine=innodb;
drop table if exists stuscore;
create table stuscore(
id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键',
sid tinyint comment '学号,外键',
score tinyint unsigned comment '成绩',
foreign key(sid) references stuinfo(id) on delete set null on update cascade
)engine=innodb;小结:
置空、级联操作中外键不能是从表的主键1.6 补充
phpstudy中MySQL默认不是严格模式,将MySQL设置成严格模式
打开my.ini,在sql-mode的值中,添加STRICT_TRANS_TABLES
sql-mode="NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES"测试
单词
medium:中等的
small:小
tiny:微小
big:大
评论 (0)