1.1 目标
- 了解MVC思想的概念;
- 理解MVC中每个组件所处理的业务;
- 理解MVC思想的优缺点;
- 掌握MVC思想的设计思路;
- 了解基于MVC思想的单一入口概念;
- 掌握MVC的实际应用;
1.2 MVC介绍
1、MVC是一个编程思想,是一种设计模式
2、思想:将一个功能分解成3个部分,M V C
Model(模型):处理与数据有关的逻辑
View(视图):显示页面
Controller(控制器):处理业务逻辑
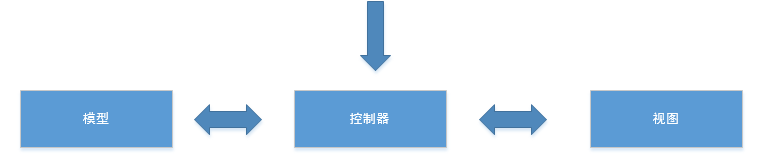
小结:
1、控制器用来接收请求
2、以后不能直接请求模型和视图
1.3 MVC演化
1.3.1 显示商品
1、导入products表的数据
2、将上一讲的MyPDO类拷贝到站点下,改名为MyPDO.class.php,这个文件中只存放MyPDO类
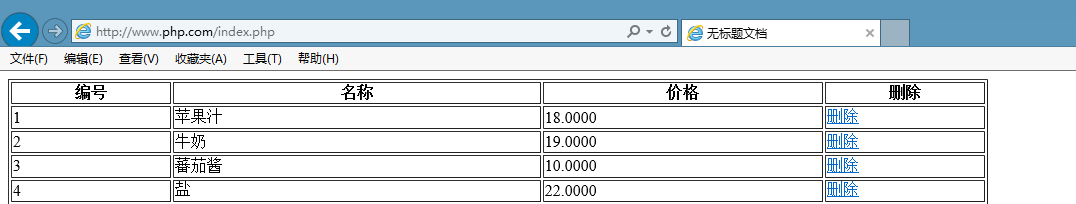
3、在站点下创建index.php,代码如下
<?php
//自动加载类
spl_autoload_register(function($class_name){
require "./{$class_name}.class.php";
});
//连接数据库
$param=array(
'user' => 'root',
'pwd' => 'root'
);
$mypdo= MyPDO::getInstance($param);
//获取商品数据
$list=$mypdo->fetchAll('select * from products');
?>
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
</head>
<body>
<table border='1' width='980' bordercolor='#000'>
<tr>
<th>编号</th> <th>名称</th> <th>价格</th> <th>删除</th>
</tr>
<?php foreach($list as $rows):?>
<tr>
<td><?=$rows['proID']?></td>
<td><?=$rows['proname']?></td>
<td><?=$rows['proprice']?></td>
<td><a href="">删除</a></td>
</tr>
<?php endforeach;?>
</table>
</body>
</html>运行结果
1.3.2 演化一:分离视图
1、创建products_list.html页面(视图页面),将显示部分的代码拷贝到视图页面上
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
</head>
<body>
<table border='1' width='980' bordercolor='#000'>
<tr>
<th>编号</th> <th>名称</th> <th>价格</th> <th>删除</th>
</tr>
<?php foreach($list as $rows):?>
<tr>
<td><?=$rows['proID']?></td>
<td><?=$rows['proname']?></td>
<td><?=$rows['proprice']?></td>
<td><a href="">删除</a></td>
</tr>
<?php endforeach;?>
</table>
</body>
</html>2、在index.php页面上加载视图
<?php
//自动加载类
spl_autoload_register(function($class_name){
require "./{$class_name}.class.php";
});
//连接数据库
$param=array(
'user' => 'root',
'pwd' => 'root'
);
$mypdo= MyPDO::getInstance($param);
//获取商品数据
$list=$mypdo->fetchAll('select * from products');
//加载视图
require './products_list.html';1.3.3 演化二:分离模型
模型的规则
1、一个表对应一个模型,表名和模型名一致(必须的)
2、模型以Model结尾(不是必须的)
代码实现:
1、在站点下创建ProductsModel.class.php页面
<?php
//products模型用来操作products表
class ProductsModel {
//获取products表的数据
public function getList() {
//连接数据库
$param=array(
'user' => 'root',
'pwd' => 'root'
);
$mypdo= MyPDO::getInstance($param);
//获取商品数据
return $mypdo->fetchAll('select * from products');
}
}2、在index.php页面中调用模型的getList()
<?php
//自动加载类
spl_autoload_register(function($class_name){
require "./{$class_name}.class.php";
});
//实例化模型
$model=new ProductsModel();
$list=$model->getList();
//加载视图
require './products_list.html';1.3.4 演化三:分离基础模型
连接数据库的代码每个模型都要使用,所有我们需要将连接数据库的代码封装到基础模型类中(Model)
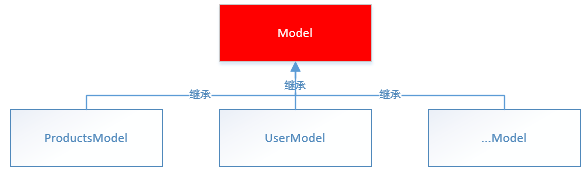
第一步:在站点下创建Model.class.php页面(基础模型)
<?php
//基础模型
class Model {
protected $mypdo;
public function __construct() {
$this->initMyPDO();
}
//连接数据库
private function initMyPDO() {
$param=array(
'user' => 'root',
'pwd' => 'root'
);
$this->mypdo= MyPDO::getInstance($param);
}
}第二步:ProductsModel继承基础模型类
<?php
//products模型用来操作products表
class ProductsModel extends Model{
//获取products表的数据
public function getList() {
return $this->mypdo->fetchAll('select * from products');
}
}1.3.5 演化四:分离控制器
控制器代码放在index.php页面中是不合理的,因为项目中的控制器会很多,而index.php只有一个。所以需要将控制器分离开来
控制器的规则:
1、一个模块对应一个控制器(必须的)
2、控制器以Controller结尾(不是必须的)
3、控制器中的方法以Action结尾(不是必须的),目的防止方法名是PHP关键字
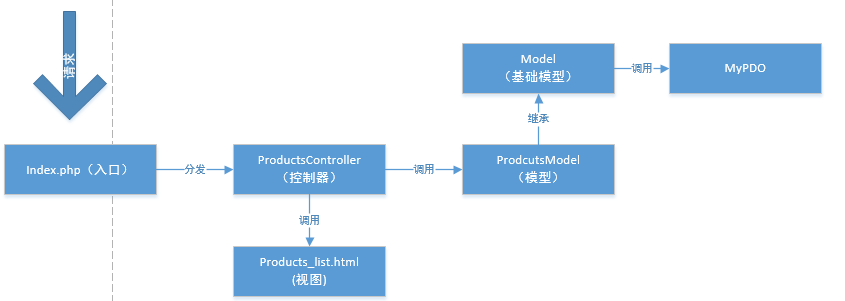
创建ProductsController.class.php
<?php
//商品模块
class ProductsController {
//获取商品列表
public function listAction() {
//实例化模型
$model=new ProductsModel();
$list=$model->getList();
//加载视图
require './products_list.html';
}
}index.php页面
<?php
//自动加载类
spl_autoload_register(function($class_name){
require "./{$class_name}.class.php";
});
//确定路由
$c=$_GET['c']??'Products'; //控制器
$a=$_GET['a']??'list'; //方法
$c=ucfirst(strtolower($c)); //首字母大写
$a=strtolower($a); //转成小写
$controller_name=$c.'Controller'; //拼接控制器类名
$action_name=$a.'Action'; //拼接方法名
//请求分发
$obj=new $controller_name();
$obj->$action_name();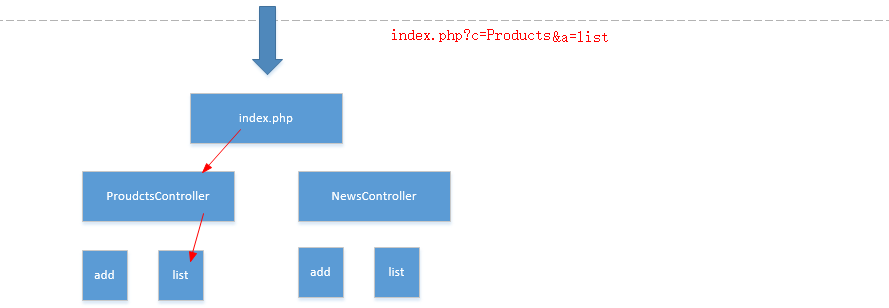
通过在url地址上传递参数来寻址。
c:控制器
a:方法
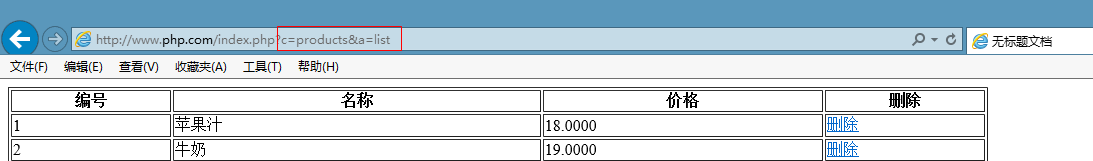
注意:每次请求都要从index.php进入。所以index.php又叫入口文件。
小结:
1.4 删除商品
入口(products_list.html)
<td><a href="index.php?c=Products&a=del&proid=<?=$rows['proID']?>" onclick="return confirm('确定要删除吗')">删除</a></td>控制器(ProductsController)
<?php
//商品模块
class ProductsController {
..
//删除商品
public function delAction() {
$id=(int)$_GET['proid']; //如果参数明确是整数,要强制转成整形
$model=new ProductsModel();
if($model->del($id))
header('location:index.php?c=Products&a=list');
else {
echo '删除失败';
exit;
}
}
}
模型(ProductsModel)
<?php
//products模型用来操作products表
class ProductsModel extends Model{
...
//删除商品
public function del($proid) {
return $this->mypdo->exec("delete from products where proid=$proid");
}
}

评论 (0)